Pediatric Ophthalmology
Hyperopia in children
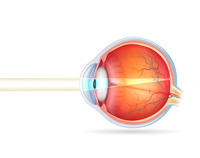
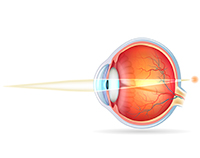
Farsightedness in children is a refractive error that causes blurred and uncomfortable vision of near (and sometimes also distant) objects. Unlike myopia, the images are focused behind the retina and not directly on it.
Children suffering from hyperopia are characterized by alterations in the different structures of the eye such as their corneal curvature, the optical power of their crystalline lens (low power) or the size of their eyeball (shorter than normal length).
Like myopia, farsightedness has an important hereditary component.
Hyperopia affects 30% of Spaniards and occurs in up to 70% of newborns.
NORMAL EYE
FARSIGHTEDNESS
Farsightedness at different ages

INFANCY
Farsightedness affects most newborns, as their eyes are not fully developed yet.
Read more
However, this visual anomaly tends to correct itself naturally, as the child grows, since his eye has a great capacity for accommodation and manages to compensate for poor vision up close.
When the problem persists and is not corrected properly, other visual disturbances can be triggered, such as lazy eye or strabismus.
Although hyperopia cannot be prevented, it is advisable to have a complete ophthalmological check-up from the age of 3-4 to detect or rule out any visual alteration that is still latent. If you have a family history or there are any previous symptoms, it is recommended to have this check-up before this age.

ADOLESCENCE
Young people with hyperopia and low prescription do not usually manifest it since they compensate for it through the effort of accommodation.

ADULTHOOD
In adults over 40 years of age, farsightedness can be confused with presbyopia or eyestrain.
However, this visual anomaly tends to correct itself naturally, as the child grows, since his eye has a great capacity for accommodation and manages to compensate for poor vision up close.
When the problem persists and is not corrected properly, other visual disturbances can be triggered, such as lazy eye or strabismus.
Although hyperopia cannot be prevented, it is advisable to have a complete ophthalmological check-up from the age of 3-4 to detect or rule out any visual alteration that is still latent. If you have a family history or there are any previous symptoms, it is recommended to have this check-up before this age.














